Market Entry Strategies are like the cool kids’ playbook for businesses looking to make it big in the global arena. From exporting to franchising and joint ventures, this topic is a must-read for those ready to rock the business world.
Overview of Market Entry Strategies
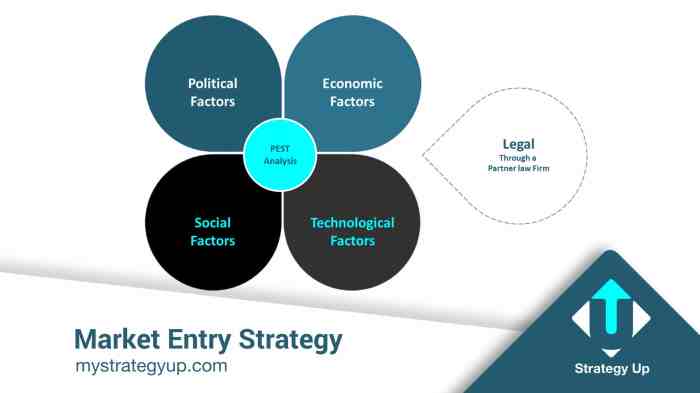
Market entry strategies are essential plans and actions that businesses use to enter new markets successfully. These strategies are crucial for companies looking to expand their reach, increase their customer base, and maximize profits. Different types of market entry strategies include exporting, franchising, joint ventures, strategic alliances, mergers, acquisitions, and greenfield investments.
Types of Market Entry Strategies
- Exporting: Selling products or services to foreign markets.
- Franchising: Allowing third parties to operate under your brand in exchange for fees and royalties.
- Joint Ventures: Partnering with a local company to enter a new market together.
- Strategic Alliances: Collaborating with another company for mutual benefit in a new market.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Buying or merging with an existing company in the target market.
- Greenfield Investments: Building new facilities or starting operations from scratch in a new market.
Factors Influencing Market Entry Strategy Selection
- Market Size and Growth Potential
- Regulatory Environment and Legal Considerations
- Cultural and Social Factors
- Competitive Landscape
- Resource Availability and Investment Requirements
Examples of Successful Market Entry Strategies
- McDonald’s: Through franchising, McDonald’s has successfully entered and expanded in markets worldwide.
- Apple: Apple entered the Chinese market through strategic alliances with local partners, leading to significant growth.
- Google: Google’s acquisition of YouTube allowed it to enter and dominate the online video-sharing market.
Exporting as a Market Entry Strategy
When a company decides to enter a new market by selling its products or services to customers in another country, it is known as exporting. This strategy involves producing goods in the home country and shipping them to be sold in the target market.
Advantages of Exporting
- Access to new markets without the need for significant investment in physical infrastructure
- Potential for increased sales and revenue by reaching a larger customer base
- Reduced risk compared to other market entry strategies like direct investment
Disadvantages of Exporting
- Dependence on intermediaries for distribution, which can reduce profit margins
- Risks associated with currency fluctuations and political instability in the target market
- Limited control over marketing and customer relationships compared to direct investment
Companies Successfully Using Exporting
One example of a company that has successfully expanded into new markets through exporting is Apple Inc. The tech giant manufactures its products in various countries and sells them globally, allowing it to reach a wide customer base while minimizing risks.
Key Considerations for Exporting
- Understanding the target market’s regulations and trade barriers
- Developing a strong distribution network or partnerships in the new market
- Adapting products or services to meet the needs and preferences of customers in the target market
Franchising as a Market Entry Strategy: Market Entry Strategies

Franchising is a market entry strategy where a business owner (franchisor) grants another individual or group (franchisee) the right to use its brand name, products, and business model in exchange for a fee or royalty. This allows the franchisee to operate their own business under the established brand name and benefit from the franchisor’s support and expertise.
Pros and Cons of Franchising for Market Entry
- Pros:
- Fast expansion: Franchising allows a business to quickly expand into new markets without significant capital investment.
- Brand recognition: Franchising leverages the established brand name of the franchisor, making it easier to attract customers.
- Local expertise: Franchisees bring local knowledge and understanding, which can be valuable in unfamiliar markets.
- Shared risk: The franchisee bears most of the financial risk, reducing the burden on the franchisor.
- Cons:
- Lack of control: Franchisors have limited control over franchisees, which can lead to inconsistencies in operations and customer experience.
- Cost: Setting up a franchise system can be expensive and time-consuming for the franchisor.
- Legal issues: Franchising involves complex legal agreements that need to be carefully drafted to protect both parties.
- Quality control: Maintaining consistent quality across all franchise locations can be challenging.
Case Studies of Global Franchising Success
One notable example of global franchising success is McDonald’s, which has expanded to over 100 countries through franchising. Another example is Subway, with more than 40,000 franchise locations worldwide.
Legal and Financial Aspects of Franchising
- Legal aspects:
- Franchise agreement: A legally binding contract outlining the terms and conditions of the franchise relationship.
- Intellectual property rights: Protection of trademarks, copyrights, and other proprietary assets.
- Compliance: Franchisors must ensure compliance with franchise laws and regulations in various countries.
- Financial aspects:
- Initial investment: Franchisees typically pay an initial fee to acquire the franchise rights.
- Royalties: Ongoing payments to the franchisor based on sales or profits.
- Marketing fees: Contributions to national or global marketing campaigns.
- Profit-sharing: Some franchisors share a percentage of profits with franchisees.
Joint Ventures and Strategic Alliances
Joint ventures and strategic alliances are collaborative agreements between two or more companies to work together towards a common goal in a specific market. In the context of market entry, these partnerships can help companies leverage each other’s strengths to enter new markets more effectively.
Benefits and Challenges of Joint Ventures and Strategic Alliances
- Benefits:
- Access to new markets and distribution channels
- Shared resources and risks
- Access to local knowledge and expertise
- Challenges:
- Potential conflicts between partners
- Loss of control over decision-making
- Cultural differences and communication barriers
Examples of Successful Joint Ventures or Strategic Alliances, Market Entry Strategies
- Starbucks and PepsiCo forming a strategic alliance to distribute ready-to-drink coffee products
- Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance for shared technology development and cost-saving synergies
- Sony-Ericsson joint venture for mobile phone development and marketing
Managing Joint Ventures and Strategic Alliances for Market Entry
- Establish clear goals and expectations from the partnership
- Communicate openly and regularly with partners to address any issues promptly
- Ensure a fair distribution of responsibilities and benefits among partners
- Regularly evaluate the performance of the joint venture/strategic alliance and make necessary adjustments