Kicking off with Understanding Sales Cycles, this topic dives deep into the crucial aspects of sales strategies and revenue growth, setting the stage for an enlightening discussion that will leave you with a new perspective on sales cycles.
Exploring the stages, factors, and strategies involved in sales cycles will provide valuable insights for businesses striving to optimize their sales processes.
Importance of Understanding Sales Cycles
Understanding sales cycles is crucial for businesses as it allows them to anticipate customer behavior, tailor their sales strategies, and ultimately drive revenue growth. By comprehending the different stages of a sales cycle, businesses can better allocate resources, identify opportunities for improvement, and maximize their sales potential.
Impact on Revenue Growth
- By analyzing sales cycles, businesses can identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies in the sales process and take corrective actions to improve conversion rates.
- Understanding sales cycles can help businesses forecast sales trends, set realistic revenue targets, and optimize their sales strategies to meet those targets.
- Aligning sales strategies with different stages of the sales cycle can lead to more effective lead nurturing, customer engagement, and ultimately, increased revenue.
Stages of a Sales Cycle
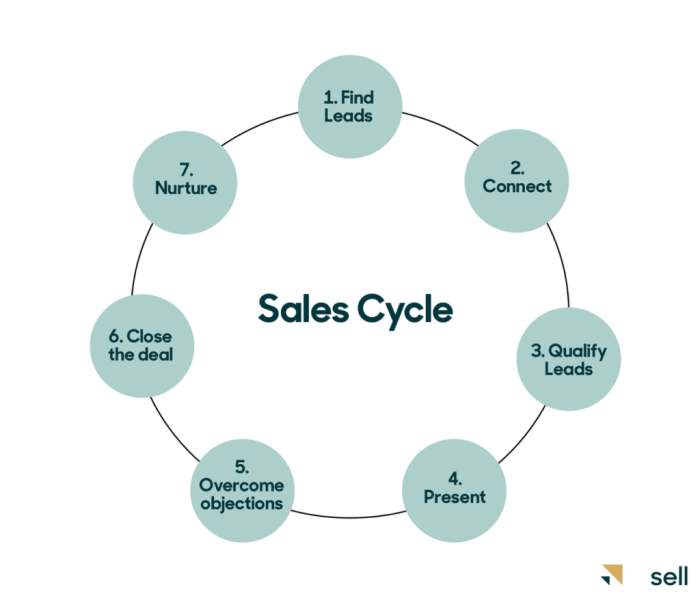
In the sales world, understanding the stages of a sales cycle is crucial for success. Each stage represents a key point in the process of turning a potential lead into a loyal customer. Let’s break down the typical stages of a sales cycle and explore the key activities involved in each stage.
1. Prospecting, Understanding Sales Cycles
The first stage of a sales cycle is prospecting. This involves identifying potential customers who may be interested in your product or service. Key activities in this stage include researching leads, collecting contact information, and determining the best approach to reach out to them.
2. Qualifying
Once leads have been identified, the next stage is qualifying. This involves determining if the leads have the potential and budget to make a purchase. Key activities in this stage include conducting needs assessments, evaluating the lead’s fit with your product or service, and gauging their level of interest.
3. Presenting and Demonstrating
After qualifying leads, the salesperson moves on to presenting and demonstrating the product or service. This stage involves showcasing the features and benefits of what you offer. Key activities include giving presentations, providing product demonstrations, and addressing any questions or concerns the lead may have.
4. Handling Objections
During the sales process, it’s common for leads to voice objections or concerns. This stage involves addressing these objections in a way that reassures the lead and helps move the sale forward. Key activities include active listening, empathizing with the lead’s concerns, and providing solutions to overcome objections.
5. Closing the Sale
The final stage of the sales cycle is closing the sale. This involves securing a commitment from the lead to make a purchase. Key activities in this stage include negotiating terms, finalizing the deal, and ensuring a smooth transition to the post-sales process.
Short Sales Cycles vs. Long Sales Cycles
Short sales cycles typically involve a quicker turnaround time from initial contact to closing the sale. These are common in industries where decisions are made swiftly, such as retail or e-commerce. On the other hand, long sales cycles involve a more extended process that may take weeks or even months to complete. These are often seen in industries with complex products or services that require thorough evaluation and decision-making.
Factors Influencing Sales Cycles: Understanding Sales Cycles
When it comes to sales cycles, various factors can influence their length and effectiveness. These factors can be either external, internal, or related to customer behavior. Understanding these influences is crucial for businesses to adapt their strategies accordingly and optimize their sales processes.
External Factors
External factors play a significant role in shaping sales cycles. These factors are often beyond the control of a company but can have a direct impact on the length of the sales cycle. Some external factors include:
- Market Conditions: Economic trends, industry competition, and market demand can all influence how long it takes for a sale to be completed.
- Regulatory Environment: Changes in regulations or policies can affect the sales process and lead to delays in closing deals.
- Seasonality: Certain industries experience fluctuations in sales volume based on seasonal trends, which can impact the length of the sales cycle.
Internal Factors
Internal factors within a company can also influence the effectiveness of a sales cycle. These factors are often within the control of the business and can be optimized to streamline the sales process. Some internal factors include:
- Sales Team Performance: The skills, training, and motivation of the sales team can impact how efficiently leads are nurtured and converted into customers.
- Product Quality and Pricing: The quality of the product or service being offered, as well as its pricing strategy, can influence the speed at which sales are closed.
- Internal Processes: The effectiveness of internal sales processes, such as lead management, CRM utilization, and communication channels, can impact the overall sales cycle.
Customer Behavior
Customer behavior is another critical factor that shapes sales cycles. Understanding how customers engage with the sales process and what influences their decision-making can help businesses tailor their strategies to better meet customer needs. Some aspects of customer behavior that influence sales cycles include:
- Buyer Persona: Different buyer personas may have varying preferences and pain points, leading to differences in the length of the sales cycle.
- Decision-Making Process: Understanding how customers make decisions, who is involved in the process, and what factors influence their choices can help businesses navigate the sales cycle more effectively.
- Communication Preferences: Aligning communication channels and messaging with customer preferences can accelerate the sales process and improve customer satisfaction.
Strategies for Optimizing Sales Cycles
In the fast-paced world of sales, optimizing your sales cycles is crucial to increase efficiency and drive revenue. By implementing effective strategies, you can accelerate the sales process, personalize your approach, and leverage data analysis to make informed decisions.
Effective Strategies for Accelerating Sales Cycles
- Utilize CRM software to track customer interactions and streamline communication.
- Implement automated email campaigns to nurture leads and keep prospects engaged.
- Offer personalized incentives or discounts to encourage faster decision-making.
- Provide timely follow-ups and address customer concerns promptly to avoid delays.
Personalizing Sales Approaches Based on Sales Cycle Stage
- During the awareness stage, focus on educating prospects and building trust through informative content.
- In the consideration stage, tailor your messaging to address specific pain points and highlight how your product/service can solve them.
- For the decision stage, offer personalized demos or trials to showcase the value of your offering and close the deal.
The Importance of Data Analysis in Optimizing Sales Cycles
Data analysis plays a crucial role in optimizing sales cycles by providing insights into customer behavior, preferences, and trends. By analyzing data from CRM systems, website analytics, and sales reports, you can identify bottlenecks, track key performance indicators, and make data-driven decisions to improve sales efficiency and effectiveness.